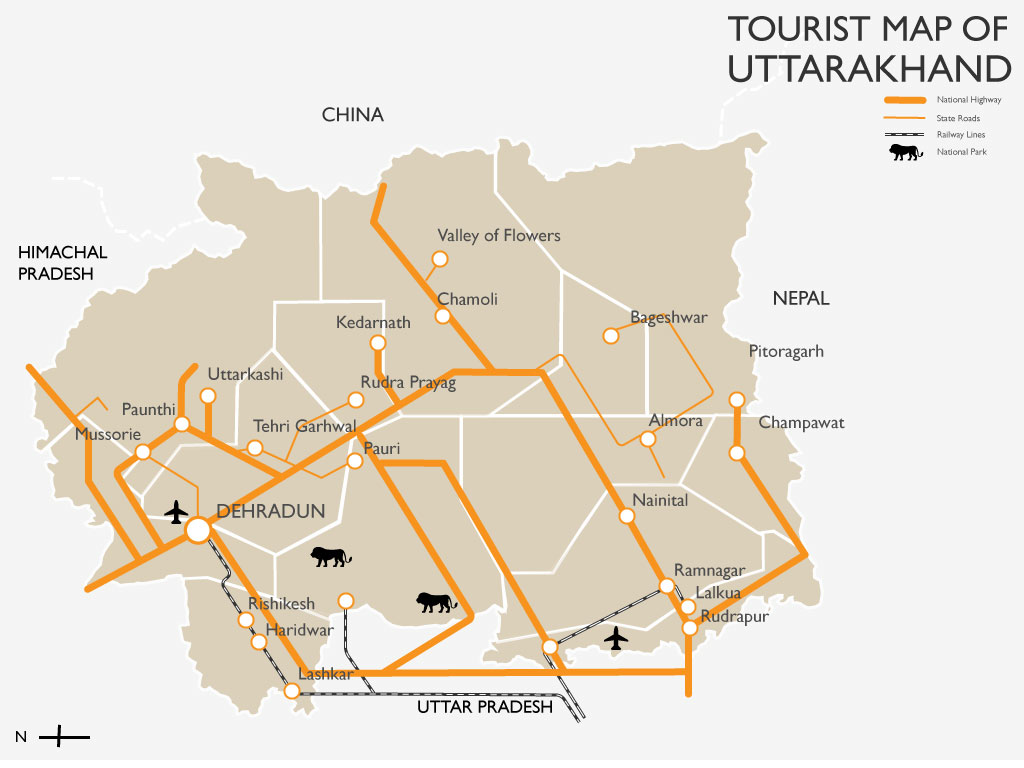
Uttarakhand, known as the “Land of Gods,” is a state rich in natural beauty, spiritual significance, and historical importance. This state, which is in the Himalayas, has a unique mix of culture, pilgrimage, excitement, and growth. If you want to do well on the UPSC civil services or state PSC exams, or if you just want to learn more about Indian geography and states in general, you need to know about Uttarakhand. This complete guide has 100 carefully researched general knowledge questions with full answers covering 11 main topics. These topics range from the holy Char Dham pilgrimage to famous people like MS Dhoni, from Jim Corbett National Park to the Ganga River’s origin to modern economic growth. You can use this full guide to learn Uttarakhand GK for tests or for your own personal use.

By Shivam Kumar 766 – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Link
- Major Rivers on Uttarakhand GK
- Wildlife & Environment
- History on Uttarakhand Gk
- Freedom Movement & Politics
- Culture & Festivals
- Language, Literature & Symbols
- Economy, Industry & Resources
- Demography & Administration
- Notable Personalities & Achievements
- Miscellaneous & Fun Facts
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. When was Uttarakhand formed as a state?
A. Uttarakhand was formed on 9th November 2000 as the 27th state of India, separated from Uttar Pradesh.
Q2. What was the original name of Uttarakhand?
A. The state was originally named Uttaranchal when it was formed in 2000. It was renamed Uttarakhand in January 2007.
Q3. What is the capital of Uttarakhand?
A. Dehradun is the administrative capital of Uttarakhand, while Nainital is the judicial capital.
Q4. What is the area of Uttarakhand?
A. Uttarakhand covers an area of 53,483 square kilometers, comprising 1.63% of India’s total land area.
Q5. What is the population of Uttarakhand according to the 2011 Census?
A. The population of Uttarakhand is 10,086,292 (approximately 1.01 crore) as per the 2011 Census.
Q6. What is the population density of Uttarakhand?
A. The population density of Uttarakhand is 189 persons per square kilometer.
Q7. How many districts does Uttarakhand have?
A. Uttarakhand has 13 districts divided into two administrative divisions: Garhwal (7 districts) and Kumaon (6 districts).
Q8. What are the two main divisions of Uttarakhand?
A. The two main divisions of Uttarakhand are Garhwal and Kumaon regions.
Q9. What percentage of Uttarakhand’s population lives in rural areas?
A. According to the 2011 Census, 69.77% of Uttarakhand’s population resides in rural areas.
Q10. What percentage of Uttarakhand’s land is covered by forests?
A. Approximately 65% of Uttarakhand’s land is covered by forests, with the state’s forest cover being 45.4% of its geographical area.

By User:GDibyendu (Original Work) – Author, Public Domain, Link
Major Rivers on Uttarakhand GK
Q11. Which is the most important river originating in Uttarakhand?
A. The Ganga (Ganges) River is the most important river, formed by the meeting of Alaknanda and Bhagirathi rivers at Devprayag.
Q12. Where does the Ganga River originate in Uttarakhand?
A. The Ganga is formed at Devprayag where the Alaknanda and Bhagirathi rivers converge.
Q13. Where does the Alaknanda River originate?
A. The Alaknanda River originates from the Satopanth Glacier near Badrinath.
Q14. Where does the Bhagirathi River originate?
A. The Bhagirathi River originates from the Gangotri Glacier in Uttarkashi district.
Q15. Name the major tributaries of the Alaknanda River.
A. The major tributaries of the Alaknanda are Mandakini, Pindar, Dhauliganga, and Nandakini.
Q16. Where does the Yamuna River originate in Uttarakhand?
A. The Yamuna River originates from the Yamunotri Glacier in Uttarkashi district.
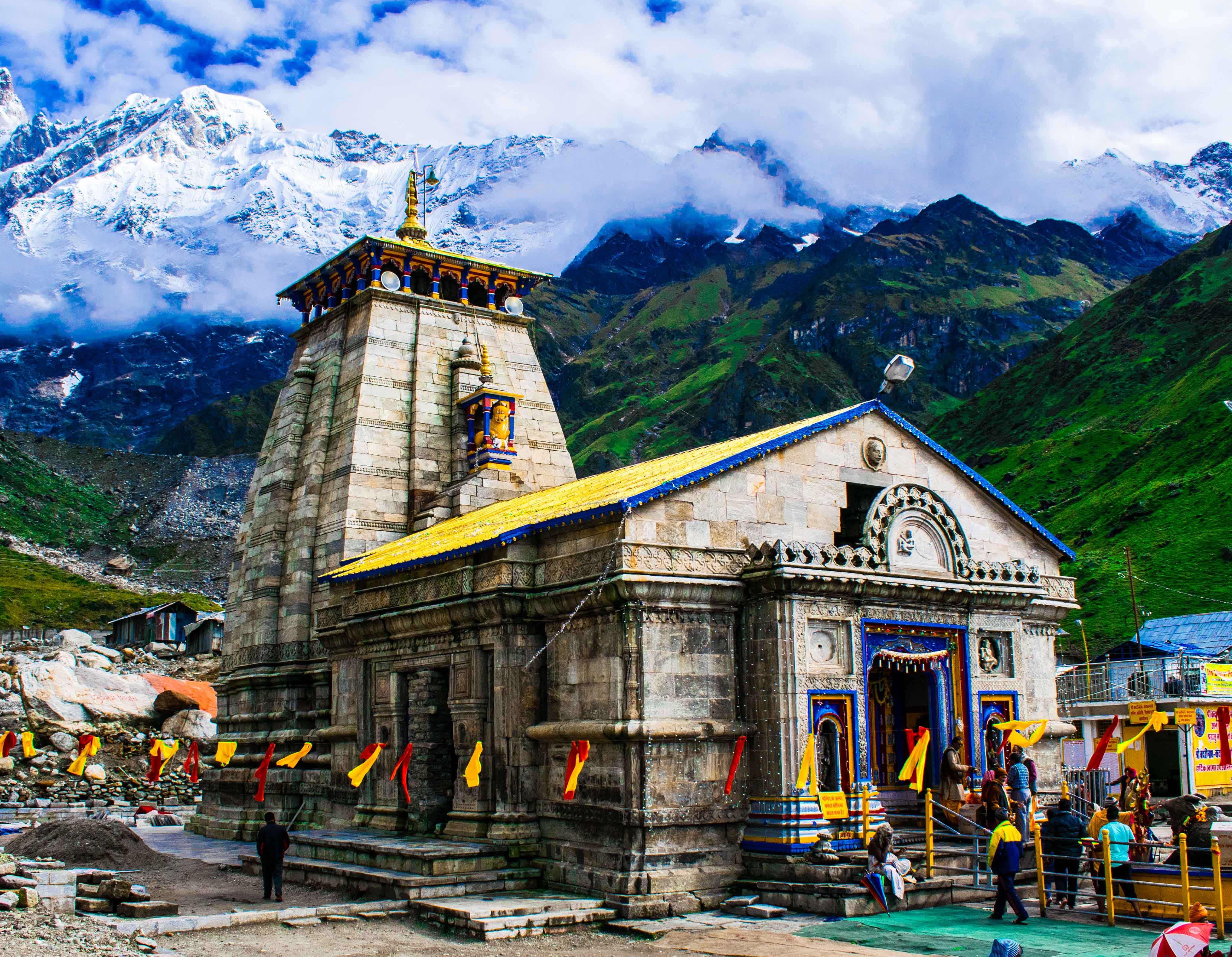
Q17. What is the significance of the Mandakini River?
A. The Mandakini River originates near Kedarnath and is associated with the sacred Kedarnath temple and the 2013 Kedarnath disaster.
Q18. Name the tributaries of the Yamuna River in Uttarakhand.
A. The major tributaries of the Yamuna in Uttarakhand are the Tons, Giri, and Hanuman Ganga rivers.
Q19. What is the Panch Prayag?
A. Panch Prayag refers to five confluences of rivers in Garhwal: Devprayag, Rudraprayag, Nandprayag, Karnaprayag, and Vishnuprayag.
Q20. How many major rivers flow through Uttarakhand?
A. Eleven major rivers flow through Uttarakhand including Ganga, Yamuna, Alaknanda, Bhagirathi, Mandakini, and others.

By Coupdoeil, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
Wildlife & Environment
Q21. How many national parks does Uttarakhand have?
A. Uttarakhand has 6 national parks including Jim Corbett National Park, Gangotri National Park, and Nanda Devi National Park.
Q22. Which is India’s oldest national park?
A. Jim Corbett National Park, established in 1936, is India’s oldest national park and the first in Asia.
Q23. When was Jim Corbett National Park established?
A. Jim Corbett National Park was established in 1936 and was originally known as Hailey National Park before being renamed.
Q24. Where is Jim Corbett National Park located?
A. Jim Corbett National Park is located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand in the foothills of the Himalayas.
Q25. What is Nanda Devi National Park famous for?
A. Nanda Devi National Park is famous for being a UNESCO World Heritage Site and home to rare species like snow leopards, Himalayan musk deer, and blue sheep.
Q26. Which is the largest national park in Uttarakhand?
A. Gangotri National Park is the largest national park in Uttarakhand.
Q27. How many wildlife sanctuaries does Uttarakhand have?
A. Uttarakhand has 7 wildlife sanctuaries including Binsar, Rajaji, and Askot Wildlife Sanctuaries.
Q28. Name the famous bird sanctuary in Uttarakhand.
A. Pangot and Kilbury Bird Sanctuary is a famous bird sanctuary home to over 580 species of birds.
Q29. What is the state animal of Uttarakhand?
A. The Musk Deer is the state animal of Uttarakhand.
Q30. What is the state bird of Uttarakhand?
A. The Himalayan Monal (also called Monal Pheasant) is the state bird of Uttarakhand.
By Raghuram. A at English Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
History on Uttarakhand Gk
Q31. What ancient kingdoms ruled the region of Uttarakhand?
A. Ancient kingdoms like the Kunindas, Mauryas, Kushanas, and later the Garhwal and Kumaon kingdoms ruled the region.
Q32. What was the ancient name for the Garhwal and Kumaon region?
A. The region was known as Kedarkhand and Manaskhand in the Puranic period.

By Underlying map: w:John George Bartholomew. Image: w:User:Fowler&fowler – Own work, Public Domain, Link
Q33. What is the significance of Harshavardhan in Uttarakhand’s history?
A. Harshavardhan was a significant historical figure but his main kingdom was centered in north India, not Uttarakhand.
Q34. Who were the Kunindas?
A. The Kunindas were early rulers of Uttarakhand who practiced Shaivism and were engaged in trade and commerce.
Q35. When did the Gurkhas conquer Uttarakhand?
A. The Gurkhas from Nepal invaded and ruled parts of Uttarakhand in the late 18th century, capturing Almora in 1791 and Garhwal in 1804.
Q36. When was the Anglo-Nepalese War fought?
A. The Anglo-Nepalese War was fought from 1814-1816, after which the British gained control of Uttarakhand.
Q37. When did the British take control of Uttarakhand?
A. The British took control of Uttarakhand after winning the Anglo-Nepalese War in 1816.
Q38. What were the two kingdoms that ruled Uttarakhand before British rule?
A. The Garhwal Kingdom and Kumaon Kingdom were the two major kingdoms that ruled Uttarakhand before British colonization.
Q39. Who established the Kuninda Kingdom in Uttarakhand?
A. The exact founder of the Kuninda Kingdom is not clearly documented, but it was one of the earliest kingdoms in the region.
Q40. What was the traditional name for Uttarakhand region in ancient times?
A. The region was traditionally known as Uttara Khand (Northern Region) or Himalayan region in ancient texts.
Freedom Movement & Politics
Q41. Who was Govind Ballabh Pant?
A. Govind Ballabh Pant was a prominent freedom fighter and the first Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh, from Uttarakhand region.
Q42. What was the role of Uttarakhand in the 1857 Revolt?
A. Uttarakhand participated actively in the 1857 Revolt against British rule, with various leaders mobilizing local resistance.
Q43. Who was Kalu Singh Mehra?
A. Kalu Singh Mehra is known as the first freedom fighter of Uttarakhand and was involved in early resistance movements.
Q44. What was the “Krantiveer” organization?
A. Krantiveer was a secret organization formed in 1857 at Besung, Champavat to mobilize resistance against British colonial rule.
Q45. Name other freedom fighters from Uttarakhand.
A. Notable freedom fighters include Veer Chandra Singh Garhwali, Badri Datt Pandey, Harish Chandra Singh Rawat, and Shridhar Pant.
Q46. What was Badri Datt Pandey’s contribution?
A. Badri Datt Pandey was a journalist and activist who propagated nationalist ideas across Uttarakhand.
Q47. Who was Veer Chandra Singh Garhwali?
A. Veer Chandra Singh Garhwali was a symbol of bravery and led several protests against British rule in Uttarakhand.
Q48. What is the significance of Harish Chandra Singh Rawat?
A. Harish Chandra Singh Rawat was involved in the Quit India Movement and peasant uprisings against British exploitation.
Q49. What was the Chipko Movement?
A. The Chipko Movement was an environmental activism with nationalist undertones, where villagers hugged trees to prevent deforestation by the British.
Q50. When was Uttarakhand separated from Uttar Pradesh?
A. Uttarakhand was separated from Uttar Pradesh and formed as an independent state on 9th November 2000.
Culture & Festivals
Q51. What are the two main languages spoken in Uttarakhand?
A. Garhwali is spoken in the Garhwal region and Kumaoni in the Kumaon region of Uttarakhand.
Q52. What is Jagar dance?
A. Jagar is a spiritual folk ritual of Uttarakhand where spirits of gods or ancestors are invoked through songs and dances performed with traditional instruments like Dhol and Damau.

By Sumita Roy Dutta – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Link
Q53. What is Chholiya dance?
A. Chholiya is a traditional sword dance of the Kumaon region performed during weddings and rituals with shields, swords, and rhythmic drum beats.
Q54. What is Jhora dance?
A. Jhora is a circular group dance performed by men and women holding hands in the Kumaon region, celebrating harvests and seasonal changes without instrumental accompaniment.
Q55. What is Chanchari Nritya?
A. Chanchari Nritya is a Kumaoni folk dance performed by groups of women singing together in circles, often at weddings and festivals like Basant Panchami and Holi.
Q56. What is Pandav Nritya?
A. Pandav Nritya (also called Pandav Leela) is a Garhwali folk dance associated with the lives of the five Pandavas from the Mahabharata, performed from November to February.

By Amitsah8888 – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Link
Q57. What is Barada Nati?
A. Barada Nati is a traditional dance of the Jaunsar-Bawar region in Garhwal with martial art-like movements, colorful attire, and high energy.
Q58. What is Langvir Nritya?
A. Langvir Nritya (Parvatiya Mallakhamb) is a dance performed in Tehri Garhwal showing physical control and reflecting Uttarakhand culture for centuries.
Q59. What traditional folk music forms are popular in Uttarakhand?
A. Popular folk music forms include Garhwali songs, Kumaoni songs, Chhopati (romantic folk duets), and songs performed during agricultural and religious activities.
Q60. What are the traditional musical instruments of Uttarakhand?
A. Traditional instruments include Dhol, Damau, Turri, Ransingha, Hudka, Dholak, and Manjira Thali.
By Noopur Varma – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
Language, Literature & Symbols
Q61. What is the official language of Uttarakhand?
A. Hindi is the official language of Uttarakhand, with Sanskrit declared as the additional official language in 2010.
Q62. When was Sanskrit made the additional official language?
A. Sanskrit was made the additional official language on 19th January 2010 by Chief Minister Ramesh Pokhriyal.
Q63. What is the state animal of Uttarakhand?
A. The Musk Deer (Alpine Musk Deer) is the state animal of Uttarakhand.
Q64. What is the state bird of Uttarakhand?
A. The Himalayan Monal (Monal Pheasant) is the state bird of Uttarakhand.
Q65. What is the state flower of Uttarakhand?
A. The Brahma Kamal is the state flower of Uttarakhand.
Q66. What is the state tree of Uttarakhand?
A. The Buransh (Rhododendron) is the state tree of Uttarakhand.
Q67. What is the state fish of Uttarakhand?
A. The Golden Mahseer is the state fish of Uttarakhand.
Q68. What is the state butterfly of Uttarakhand?
A. The Common Peacock is the state butterfly of Uttarakhand.
Q69. What is the state fruit of Uttarakhand?
A. The Kafal is the state fruit of Uttarakhand.
Q70. What does the state emblem of Uttarakhand depict?
A. The state emblem is diamond-shaped featuring three mountains topped by Ashoka’s Lion Capital with streams of the Ganga below, symbolizing truth and prosperity.
Economy, Industry & Resources
Q71. What are the main economic sectors of Uttarakhand?
A. The main sectors are Services (including tourism and IT), Agriculture, Hydroelectric power, Manufacturing, and Pharmaceuticals.
Q72. What is the major crop produced in Uttarakhand?
A. Wheat, rice, and sugarcane are major crops, along with horticulture products like apples, pears, and peaches.
Q73. What is Uttarakhand known for in terms of tourism?
A. Uttarakhand is known as the “Land of Gods” for its numerous hill stations, pilgrimage sites, wildlife parks, and trekking routes.
Q74. What is the role of Hydroelectric power in Uttarakhand?
A. Hydroelectric power is a significant source of renewable energy, with the state having great potential for small hydropower projects.
Q75. What is the contribution of the IT sector in Uttarakhand’s economy?
A. The IT sector is expanding across the state, contributing to the service sector’s growth and job creation.
Q76. What industrial sectors are emerging in Uttarakhand?
A. Emerging sectors include pharmaceuticals, Ayurveda and herbal medicine, MSME (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises), and biotechnology.
Q77. What is the state’s literacy rate?
A. Uttarakhand’s literacy rate is 78.82% according to the 2011 Census, with male literacy at 87.40% and female at 70.01%.
Q78. What is the highest literacy rate district in Uttarakhand?
A. Dehradun has the highest literacy rate at 84.25%.
Q79. What percentage of Uttarakhand’s GSDP comes from the Services sector?
A. The Services sector is the largest contributor to Uttarakhand’s Gross State Domestic Product.
Q80. What are the main challenges to Uttarakhand’s economic development?
A. Challenges include mountainous terrain, limited infrastructure, seasonal variations affecting agriculture, and the need for sustainable tourism development.
Demography & Administration
Q81. What was the total population of Uttarakhand in 2011?
A. The total population was 10,086,292 according to the 2011 Census.
Q82. What is the sex ratio in Uttarakhand?
A. The sex ratio in Uttarakhand varies by district, with some districts having higher ratios like Almora (1139 females per 1000 males).
Q83. How many divisions are in Uttarakhand?
A. Uttarakhand has 2 administrative divisions: Garhwal and Kumaon.
Q84. Who is the Governor of Uttarakhand?
A. Baby Rani Maurya is the current Governor of Uttarakhand (as of recent administration).
Q85. How many Lok Sabha seats does Uttarakhand have?
A. Uttarakhand has 5 Lok Sabha seats and 3 Rajya Sabha seats in the Indian Parliament.
Notable Personalities & Achievements
Q86. Who is MS Dhoni and his connection to Uttarakhand?
A. MS Dhoni, the famous Indian cricket captain, has roots in Uttarakhand through his parents’ village Lvali in Almora district, though he was born in Ranchi.
Q87. What are MS Dhoni’s major cricket achievements?
A. Dhoni captained India to victories in the 2007 ICC World Twenty20, 2011 ICC Cricket World Cup, 2013 ICC Champions Trophy, and the 2007-08 CB Series.
Q88. Who is Rishabh Pant?
A. Rishabh Pant is a professional cricketer born in Roorkee, Uttarakhand to a Kumaoni Brahmin family, now playing for Delhi and national teams.
Q89. Who is Abhinav Bindra?
A. Abhinav Bindra is a renowned shooter from Uttarakhand who has won national and international shooting championships and the Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna Award.
Q90. What is the significance of Mir Ranjan Negi from Uttarakhand?
A. Mir Ranjan Negi was a hockey player from Almora district whose life story was depicted in the Bollywood film “Chak de India.”
Q91. Who is Bachendri Pal?
A. Bachendri Pal is a mountaineer from Uttarakhand, known for her achievements in high-altitude mountaineering and expeditions.
Q92. Who are Tashi and Nungshi Malik?
A. Tashi and Nungshi Malik are twin mountaineers from Uttarakhand known for their mountaineering achievements and expeditions.
Q93. Who is Ekta Bisht?
A. Ekta Bisht, born in Almora district, is the first Indian woman cricketer to represent Uttarakhand and India in international cricket.
Q94. Who is Unmukt Chand?
A. Unmukt Chand is a cricketer from Pithoragarh district who won the ICC Under-19 World Cup and has played IPL matches.
Q95. Who is Manish Pandey?
A. Manish Pandey is an international cricketer born in Nainital, Uttarakhand, and was the first Indian to score a century in IPL.
Miscellaneous & Fun Facts
Q96. What is the Char Dham pilgrimage?
A. Char Dham (Four Abodes) is a sacred pilgrimage circuit comprising Yamunotri, Gangotri, Kedarnath, and Badrinath temples in Garhwal.
Q97. Who established the Char Dham pilgrimage circuit?
A. The great Hindu philosopher and reformer Adi Shankaracharya initiated the Char Dham yatra in the 8th century to revive Hinduism.
Q98. In which order is the Char Dham yatra traditionally undertaken?
A. The traditional order is Yamunotri, then Gangotri, followed by Kedarnath, and finally Badrinath (from west to east).
Q99. What was the significance of the 2013 Kedarnath disaster?
A. The 2013 Kedarnath disaster caused by flash floods and landslides resulted in significant loss of lives and property, affecting the Mandakini River area.
Q100. What is the state motto of Uttarakhand?
A. “Satyameva Jayate” (Truth Alone Triumphs) is the state motto of Uttarakhand, adopted from the national motto of India.
Conclusion
Uttarakhand is a state whose natural beauty, spiritual legacy, and contemporary advancements combine to create a genuinely remarkable identity. The state’s geography, culture, pilgrimage routes, natural treasures, economic progress, and noteworthy individuals are all well explained in this extensive collection of 100 Uttarakhand GK questions with detailed answers. This guide covers every important subject in an easy-to-follow format, whether you’re getting ready for the UPSC, State PSC, police, teaching examinations, or school-level quizzes.
You now have a strong knowledge base that will support both exam preparation and general awareness after studying topics including the Char Dham, the sources of the Ganga, Jim Corbett National Park, historical landmarks, and contemporary development indicators. To improve your command of Uttarakhand GK, use this resource as a long-term reference, make frequent revisions, and keep up with new developments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What does this Uttarakhand GK guide include?
This guide contains 100 well-researched questions with detailed answers covering geography, history, culture, wildlife, economy, tourism, and important personalities of Uttarakhand.
2. Is this useful for competitive exam preparation?
Yes, it is highly useful for UPSC, State PSC, UKPSC, Police Exams, Teaching Exams, and various government recruitment tests where state-specific GK is essential.
3. Are the questions beginner-friendly?
Absolutely. The questions are presented in a simple, easy-to-understand format suitable for both beginners and advanced learners.






























Leave a Comment